
The twilight time between fully awake and sound asleep may be packed with creative potential.
People who recently drifted off into a light sleep later had problem-solving power, scientists report December 8 in Science Advances. The results help demystify the fleeting early moments of sleep and may even point out ways to boost creativity.
Prolific inventor and catnapper Thomas Edison was rumored to chase those twilight moments. He was said to fall asleep in a chair holding two steel ball bearings over metal pans. As he drifted off, the balls would fall. The ensuing clatter would wake him, and he could rescue his inventive ideas before they were lost to the depths of sleep.
Delphine Oudiette, a cognitive neuroscientist at the Paris Brain Institute, and colleagues took inspiration from Edison’s method of cultivating creativity. She and her colleagues brought 103 healthy people to their lab to solve a tricky number problem. The volunteers were asked to convert a string of numbers into a shorter sequence, following two simple rules. What the volunteers weren’t told was that there was an easy trick: The second number in the sequence would always be the correct final number, too. Once discovered, this cheat code dramatically cut the solving time.
After doing 60 of these trials on a computer, the volunteers earned a 20-minute break in a quiet, dark room. Reclined and holding an equivalent of Edison’s “alarm clock” (a light drinking bottle in one dangling hand), participants were asked to close their eyes and rest or sleep if they desired. All the while, electrodes monitored their brain waves.
About half of the participants stayed awake. Twenty-four fell asleep and stayed in the shallow, fleeting stage of sleep called N1. Fourteen people progressed to a deeper stage of sleep called N2.
After their rest, participants returned to their number problem. The researchers saw a stark difference between the groups: People who had fallen into a shallow, early sleep were 2.7 times as likely to spot the hidden trick as people who didn’t fall asleep, and 5.8 times as likely to spot it as people who had reached the deeper N2 stage.
Such drastic differences in these types of experiments are rare, Oudiette says. “We were quite astonished by the extent of the results.” The researchers also identified a “creative cocktail of brain waves,” as Oudiette puts it, that seemed to accompany this twilight stage — a mixture of alpha brain waves that usually mark relaxation mingled with the delta waves of deeper sleep.
The study doesn’t show that the time spent in N1 actually triggered the later realization, cautions John Kounios, a cognitive neuroscientist at Drexel University in Philadelphia who cowrote the 2015 book The Eureka Factor: Aha Moments, Creative Insight, and the Brain. “It could have been possible that grappling with the problem and initiating an incubation process caused both N1 and the subsequent insight,” he says, making N1 a “by-product of the processes that caused insight rather than the cause.”
More work is needed to untangle the connection between N1 and creativity, Oudiette says. But the results raise a tantalizing possibility, one that harkens to Edison’s self-optimizations: People might be able to learn to reach that twilight stage of sleep, or to produce the cocktail of brain waves associated with creativity on demand.
It seems Edison was onto something about the creative powers of nodding off. But don’t put too much stock in his habits. He is also said to have considered sleep “a criminal waste of time.”
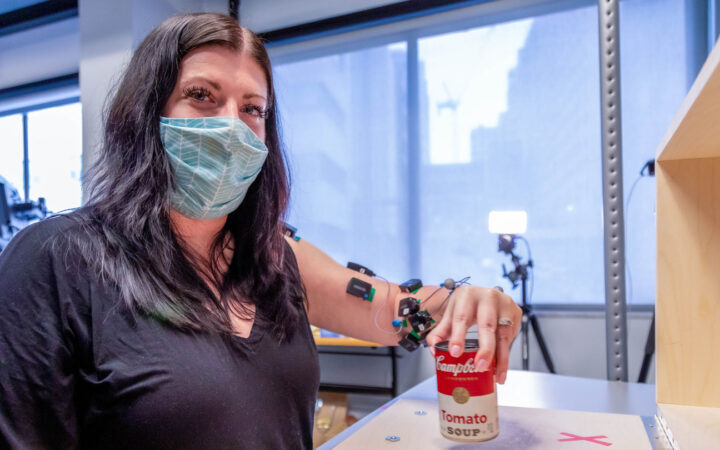
 A new treatment could restore some mobility in people paralyzed by strokes
A new treatment could restore some mobility in people paralyzed by strokes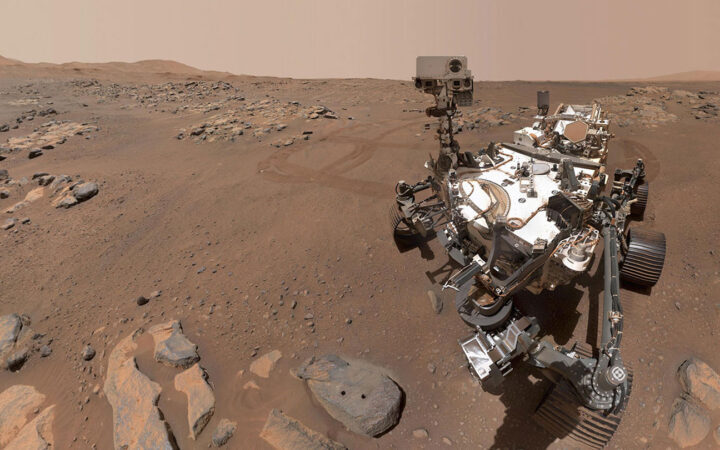  What has Perseverance found in two years on Mars?
What has Perseverance found in two years on Mars?  This robot automatically tucks its limbs to squeeze through spaces
This robot automatically tucks its limbs to squeeze through spaces  Greta Thunberg’s new book urges the world to take climate action now
Greta Thunberg’s new book urges the world to take climate action now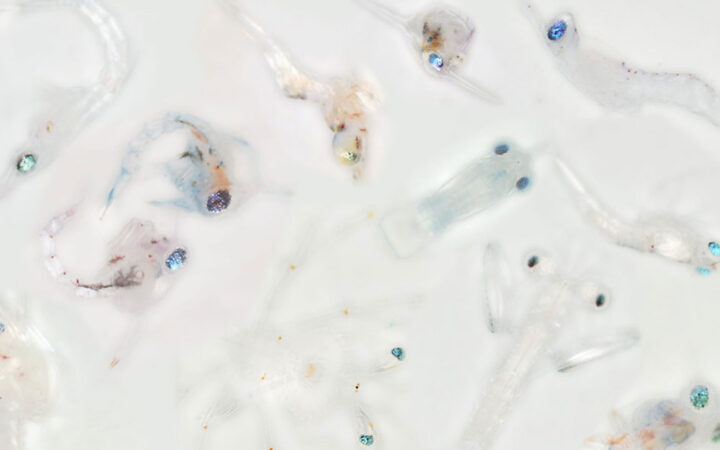  Glassy eyes may help young crustaceans hide from predators in plain sight
Glassy eyes may help young crustaceans hide from predators in plain sight  A chemical imbalance doesn’t explain depression. So what does?
A chemical imbalance doesn’t explain depression. So what does?